Networking Essentials ( Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Answers
1. Match the type of malware with the definition.
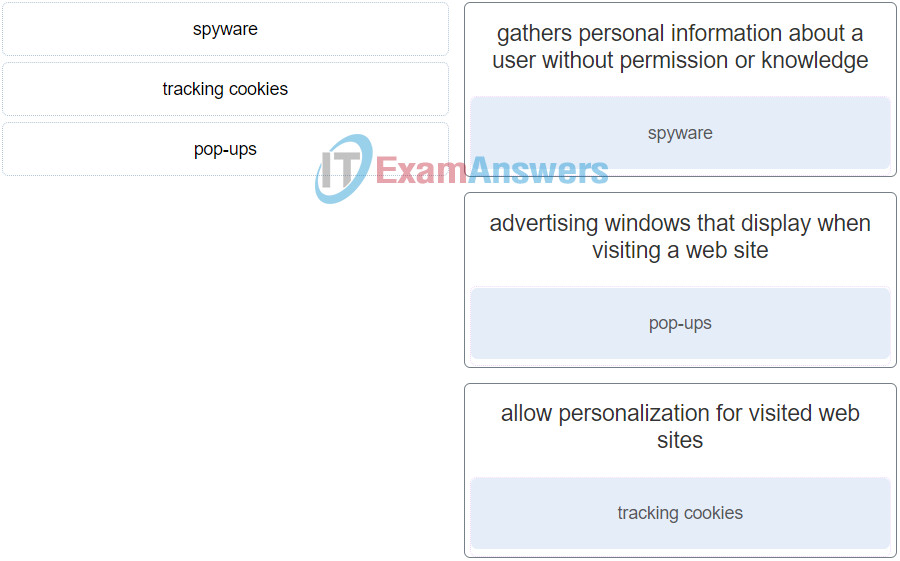
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q1
2. An intruder tries a large number of possibilities in rapid succession to guess a password. As a result, other users on the network are locked out. What type of attack has occurred?
- brute force
- ping of death
- DDoS
- SYN flooding
3. Which three attacks exploit human behavior? (Choose three.)
- zombies
- vishing
- phishing
- brute force
- malware
- pretexting
4. What is the effect of setting the security mode to WEP on a small wireless router?
- It translates IP addresses into easy-to-remember domain names.
- It allows the access point to inform clients of its presence.
- It encrypts data between the wireless client and the access point.
- It identifies the wireless LAN.
- It translates an internal address or group of addresses into an outside, public address.
5. Which solution allows external users to access only an internal FTP server on a private network?
- dynamic NAT
- NAT with overload
- port forwarding
- static NAT
6. What is an inherent security vulnerability of SSID broadcasting?
- It broadcasts the identity of the network.
- It allows unauthenticated access to the wireless network.
- It allows any host to join the wireless network.
- It sends traffic unencrypted between the wireless access point and the client.
7. Refer to the exhibit. A newly purchased client laptop has just connected to the local area network. The local area network is using a wireless router that is providing dynamic addressing as shown. Which IP address does the laptop use as a destination address when requesting a dynamically assigned address?
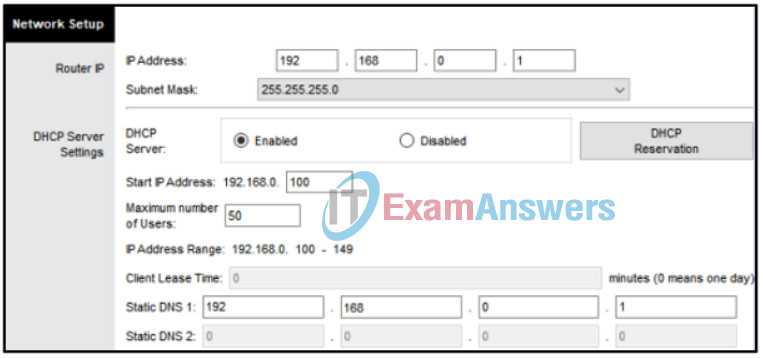
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q7
- 255.255.255.0
- 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.0.100
- 255.255.255.255
- 192.168.0.255
8. A DHCP server is used to assign IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The address pool is configured with 192.168.10.0/24. There are 3 printers on this network that need to use reserved static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP addresses in the pool are left to be assigned to other hosts?
- 252
- 254
- 253
- 251
9. Match each DHCP message type with its description. (Not all options are used.)
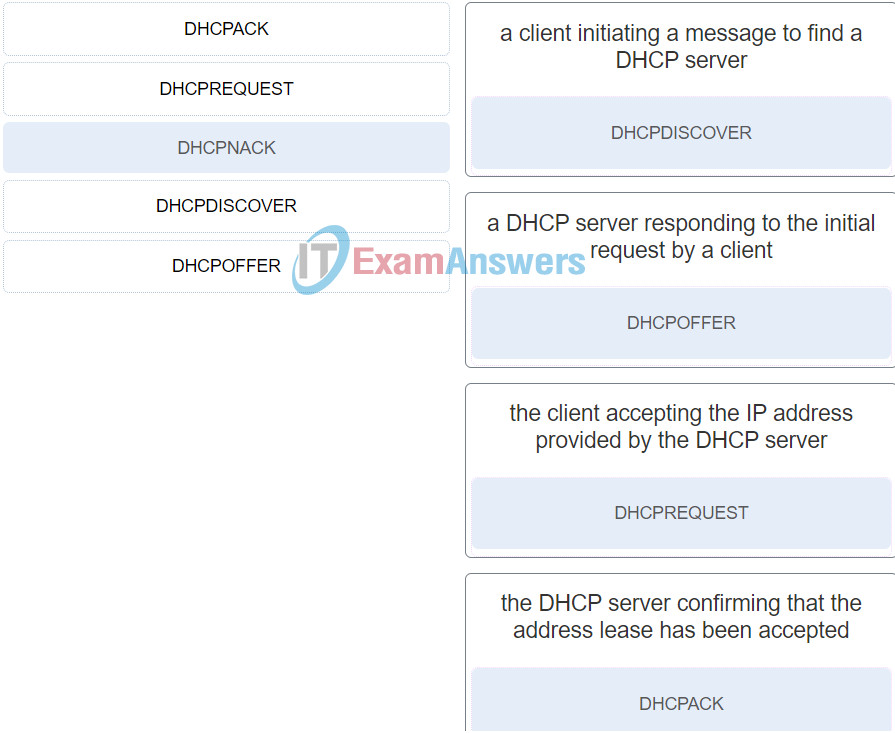
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q9
10. A client device on an Ethernet segment needs an IP address in order to communicate on the network. A DHCP server with IP address 192.168.1.1 has been configured and enabled on the network. How will a client device obtain a usable IP address for this network?
- Use a statically configured IP address from the pool of IP addresses that is offered by the DHCP server.
- Send a DHCPREQUEST packet to IP address 255.255.255.255.
- Send a DHCPDISCOVER message to physical address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
- Send a DHCPACK packet to the default gateway address.
11. Which two criteria are used to help select a network medium for a network? (Choose two.)
- the distance the selected medium can successfully carry a signal
- the environment where the selected medium is to be installed
- the number of intermediate devices that are installed in the network
- the types of data that need to be prioritized
- the cost of the end devices that are used in the network
12. What is an advantage of using standards to develop and implement protocols?
- Different manufacturers are free to apply different requirements when implementing a protocol.
- Standards provide flexibility for manufacturers to create devices that comply with unique requirements.
- Products from different manufacturers can interoperate successfully.
- A particular protocol can only be implemented by one manufacturer.
13. At which layer of the OSI model would a logical address be added during encapsulation?
- physical layer
- network layer
- data link layer
- transport layer
14. Which wireless RF band do IEEE 802.11b/g devices use?
- 2.4 GHz
- 900 MHz
- 60 GHz
- 5 GHz
15. Refer to the exhibit. Which router port connects to the modem provided by the service provider?
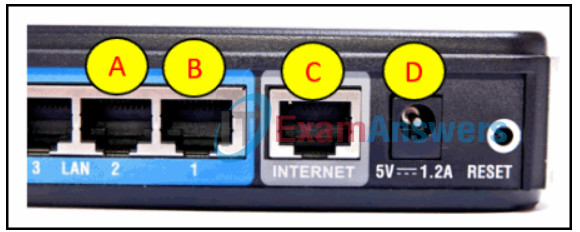
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q15
- A
- B
- C
- D
16. Which type of device filtering can be enabled on some wireless access points or wireless routers?
- authentication
- user ID
- MAC address
- IP address
17. Using a systematic troubleshooting approach, a help desk technician suspects a problem at Layer 3 of the OSI model. In gathering information, which two questions are associated with Layer 3? (Choose two.)
- From the PC, is the default gateway reachable using the ping command?
- Is there a link light on the network card?
- Is the PC configured for DHCP?
- Is the network cable plugged in?
- Does a browser connection to www.cisco.com work?
18. A customer calls the help line to report a computer problem. The help line technician responds and works with the customer for some time. However, the technician cannot identify the root cause of the problem. What should the technician do to help the customer?
- Tell the customer that a ticket is created and another technician will contact the user soon.
- Tell the customer that a replacement computer will be shipped immediately.
- Suggest that the customer visit the support website for more detailed information.
- Ask for the email address of the customer in order to send all the support documents for the computer.
19. During a move, employee workstations were disconnected from the network and reconnected in new offices. However, after the move a few workstations cannot get a valid IP address. What should be checked first to identify the root cause of the problem?
- Test if these workstations can ping the default gateway.
- Install all software updates.
- Check the operation status of the DHCP server.
- Make sure the cables are functional and properly plugged.
20. A user is setting up a home wireless network. Which type of device must the user have in order to establish the wireless network and provide access to the internet for multiple home devices?
- switch
- hub
- wireless router
- patch panel
21. A consumer places a smartphone close to a pay terminal at a store and the shopping charge is successfully paid. Which type of wireless technology was used?
- NFC
- Wi-Fi
- 3G
- Bluetooth
22. When troubleshooting network problems, where would a network administrator find the configuration information, such as the computer names and the IP addresses that are used?
- DNS server
- logical topology diagram
- physical topology diagram
- DHCP server
23. Which network migration technique encapsulates IPv6 packets inside IPv4 packets to carry them over IPv4 network infrastructures?
- tunneling
- encapsulation
- dual-stack
- translation
24. A small accounting office is setting up a wireless network to connect end devices and to provide internet access. In which two scenarios does a wireless router perform Network Address Translation (NAT)? (Choose two.)
- when a host is sending packets to a remote site owned by the manufacturer of the wireless router in order to request a digital copy of the device manual
- when a host is sending HTTP packets to the wireless router in order to update the network addressing of the LAN
- when a host is sending packets to the ISP in order to request a speed increase for Internet services==
- when a host is sending a print job to a network printer on the LAN
- when a host is sending packets to a local server in order to update the network media settings and music playlists
25. If the default gateway is configured incorrectly on a host, what is the impact on communications?
- The host is unable to communicate with hosts on both the local and remote networks.
- The host is unable to communicate on the local network.
- The host is unable to communicate with hosts on remote networks.
- The host cannot get an IP address from the DHCP server.
26. What are two common media used in networks? (Choose two.)
- wood
- fiber
- water
- copper
- nylon
27. Which two types of interference may affect the data throughput on UTP cables? (Choose two.)
- temperature
- crosstalk
- noise
- EMI
- moisture
28. What are two wiring schemes defined by the TIA/EIA organization for Ethernet installation in homes and businesses? (Choose two.)
- T568B
- T568A
- STP
- UTP
- RJ-45
29. A host needs to reach another host on a remote network, but the ARP cache has no mapping entries. To what destination address will the host send an ARP request?
- the unicast MAC address of the remote host
- the unicast IP address of the remote host
- the broadcast MAC address
- the subnet broadcast IP address
30. Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
- source MAC address
- destination MAC address
- destination IP address
- source IP address
31. What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.
- It assists in protocol design.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
- It speeds up packet delivery.
32. Which two devices are considered end devices? (Choose two.)
- router
- laptop
- hub
- switch
- printer
33. Which factor does not influence throughput?
- the operating system that is used by end devices
- the amount of data that is being sent and received on the connection
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices encountered between source and destination
- the type of data that is being transmitted
34. What is a characteristic of a peer-to-peer application?
- The resources required for the application are centralized.
- Each device can act both as a client and a server, but not simultaneously.
- Each device using the application provides a user interface and runs a background service.
- Both devices initiate a three-way handshake to determine who is initiating the communication.
35. Using default settings, what is the next step in the switch boot sequence after the IOS loads from flash?
- Search for a backup IOS in ROM.
- Load the bootstrap program from ROM.
- Load the running-config file from RAM.
- Locate and load the startup-config file from NVRAM.
- Perform the POST routine.
36. Which two files, if found, are copied into RAM as a router with the default configuration register setting boots up? (Choose two.)
- running configuration
- startup configuration
- POST diagnostics
- IOS image file
37. What are two features of protocols used within the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- The Internet Layer IP protocol has built in mechanisms for ensuring the reliable transmission and receipt of data.
- TCP mechanisms retransmit data when an acknowledgment is not received from the destination system within a set period of time.
- The same Transport Layer source port is used for all of the tabs opened at the same time within a web browser.
- TCP and UDP destination port numbers are dynamically generated by the sending device in order to track the responses to requests.
- UDP is used when an application must be delivered as quickly as possible and some loss of data can be tolerated.
38. A student is uploading files from a phone to a server on another network. Which layer of the TCP/IP model is responsible for providing an addressing scheme to transmit the data between the devices?
- transport
- application
- network access
- internet
39. Which statement correctly describes data transmission at the transport layer?
- A single datagram can include both a TCP and a UDP header.
- Both UDP and TCP use port numbers.
- Segmentation is provided by sequence numbers when UDP is used.
- Segmentation is provided by the window size field when the TCP protocol is used.
- Retransmission of lost packets is provided by both TCP and UDP.
40. What type of technology converts analog voice signals into digital data?
- SNMP
- POP3
- VoIP
- SMTP
41. Match the protocol with the function. (Not all options are used.)
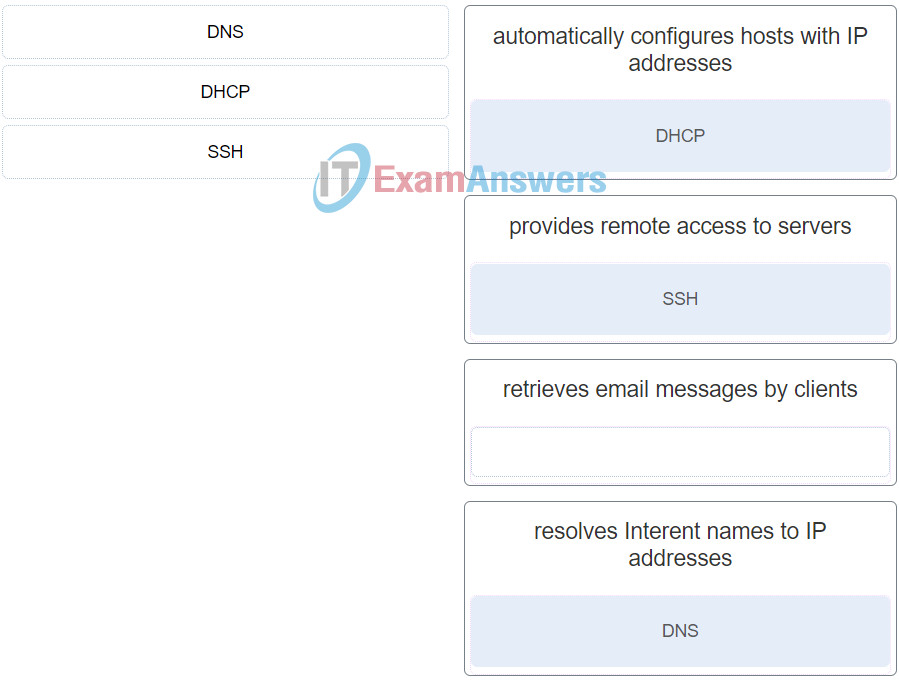
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q41
42. While a network security product is being deployed, a customizable list of allowable protocols is shown. Which three protocols should be allowed to provide for the use of email on a network? (Choose three.)
- SMTP
- IMAP4
- Telnet
- DNS
- POP3
- HTTP
- TFTP
43. In software defined network architecture, what function is removed from network devices and performed by an SDN controller?
- application policies
- control plane
- security
- data plane
44. A user is configuring a wireless access point and wants to prevent any neighbors from discovering the network. What action does the user need to take?
- Enable WPA encryption.
- Configure a DNS server.
- Configure DMZ settings.
- Disable SSID broadcast.
45. A data center has recently updated a physical server to host multiple operating systems on a single CPU. The data center can now provide each customer with a separate web server without having to allocate an actual discrete server for each customer. What is the networking trend that is being implemented by the data center in this situation?
- maintaining communication integrity
- online collaboration
- virtualization
- BYOD
46. A network administrator installs a network device that focuses on interconnecting independent local networks. At which layer of devices does this technology reside?
- access
- internet
- core
- distribution
47. A computer has to send a packet to a destination host in the same LAN. How will the packet be sent?
- The packet will be sent to the default gateway first, and then, depending on the response from the gateway, it may be sent to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will first be sent to the default gateway, and then from the default gateway it will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent only to the default gateway.
48. If the default gateway is configured incorrectly on the host, what is the impact on communications?
- There is no impact on communications.
- The host is unable to communicate on the local network.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on the local network, but is unable to communicate with hosts on remote networks.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on remote networks, but is unable to communicate with hosts on the local network.
49. Which three commands are used to set up secure access to a router through a connection to the console interface? (Choose three.)
- interface fastethernet 0/0
- line console 0
- line vty 0 4
- password cisco
- login
- enable secret cisco
50. A network administrator establishes a connection to a switch via SSH. What characteristic uniquely describes the SSH connection?
- direct access to the switch through the use of a terminal emulation program
- remote access to the switch through the use of a telephone dialup connection
- on-site access to a switch through the use of a directly connected PC and a console cable
- remote access to a switch where data is encrypted during the session
- out-of-band access to a switch through the use of a virtual terminal with password authentication
51. Which type of access is secured on a Cisco router or switch with the enable secret command?
- privileged EXEC
- console line
- AUX port
- virtual terminal
52. When configuring SSH on a router to implement secure network management, a network engineer has issued the login local and transport input ssh line vty commands. What three additional configuration actions have to be performed to complete the SSH configuration? (Choose three.)
- Configure role-based CLI access.
- Create a valid local username and password database.
- Set the user privilege levels.
- Configure the correct IP domain name.
- Generate the asymmetric RSA keys.
- Manually enable SSH after the RSA keys are generated.
53. Match the commands to the correct actions. (Not all options are used.)

Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q53
54. What is the purpose of the subnet mask in conjunction with an IP address?
- to uniquely identify a host on a network
- to determine the subnet to which the host belongs
- to mask the IP address to outsiders
- to identify whether the address is public or private
55. Which two statements describe characteristics of network addresses? (Choose two.)
- A valid public IPv4 or IPv6 address is needed in order for devices to communicate over the internet.
- DHCP is used to dynamically assign both MAC and IP addresses to devices connected to the network.
- A statically assigned IP address will be valid on any network to which the device connects.
- The MAC address of a device will change when that device moves from one Ethernet network to another.
- A MAC address is also referred to as a physical address because it is permanently embedded on the NIC.
56. What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- The range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved to reach multicast groups on a local network.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
57. Match the router prompt to the configuration task.
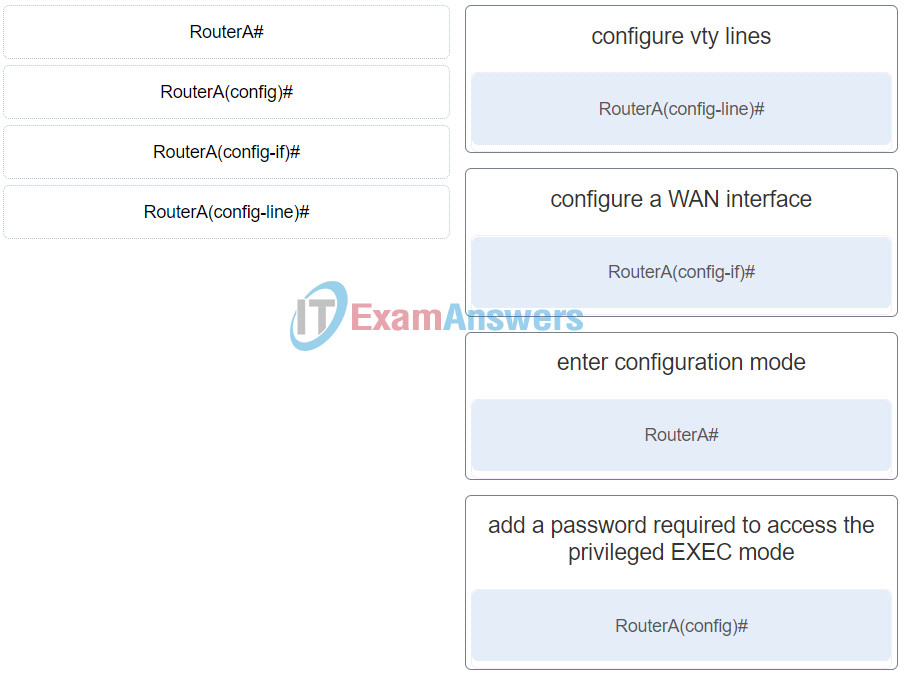
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q57
58. A network administrator issues the Switch(config)# Interface FastEthernet 0/1 command on a Cisco switch. Which term is used to describe the “0/1” part in the command?
- argument
- keyword
- hot key
- command
59. Refer to the exhibit. What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
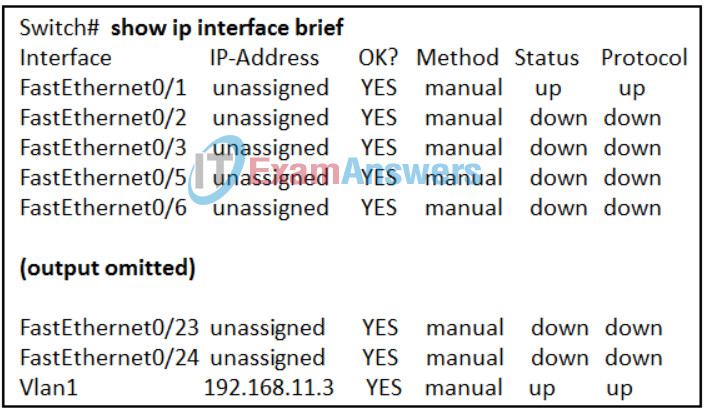
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Practice Final Exam Q59
- Passwords have been configured on the switch.
- One device is attached to a physical interface.
- The switch can be remotely managed.
- Two physical interfaces have been configured.
- The default SVI has been configured.
- Two devices are attached to the switch.
60. Which command can an administrator execute to determine what interface a router will use to reach remote networks?
- show ip route
- show arp
- show protocols
- show interfaces
61. A host needs to reach another host on a remote network, but the ARP cache has no mapping entries. To what destination address will
- the host send an ARP request?
- the unicast IP address of the remote host
- the unicast MAC address of the remote host
- the subnet broadcast IP address
- the broadcast MAC address
62. An intruder tries a large number of possibilities in rapid succession to guess a password. As a result, other users on the network are
- locked out. What type of attack has occurred?
- brute force
- ping of death
- DDoS
- SYN flooding








Linux Foundation CKA exact questions answer always keeps candidates up to date with the Certified Kubernetes Administrator Exam syllabus. Anyone who has registered with Myexamcollection Linux Foundation CKA exam questions gets exclusive access to the updated version of all the valid CKA dumps. Free updates for up to three months.
ReplyDelete